Electrostimulation is a technique that has been used for decades in the field of physiotherapy. The principle of electrostimulation, also known as “EMS”, is both simple and complex: electrodes are placed on the muscles to make them contract involuntarily.
Initially used in the medical field, electrostimulation is now exploited in the sectors of aesthetic care, well-being and sport. To make it more comfortable and optimize its use, the electrodes are now hermetically housed in partial or integral combinations.
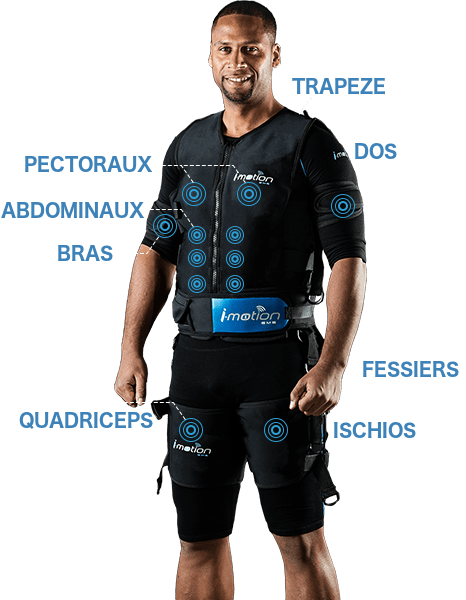
With these suits, also called “jackets”, the electrodes are positioned on the body of the practitioner in such a way that a large number of muscles are solicited during the static or dynamic treatments.

1. The EMS works like a brain
Normally, each of our movements is the result of a deliberate signal sent by our brain to one or more muscles.
In other words, the origin of the movement is in the brain and takes place in 3 stages:
- The brain sends the signal to the nerve.
- The muscle is activated by the nerve.
- The desired movement is then performed.
The role of the EMS is to momentarily “short circuit” the action of the brain; in electrostimulation, it is the machine that sends the electrical impulses, thus temporarily playing the role of the brain. It is therefore the machine that sends the signal to the electrode connected to the muscle and stimulates its contraction, without any risk for the body and the nervous system.
2 . EMS is still used in physiotherapy and sports training.
In physiotherapy, electrostimulation is used for people who are unable to perform a particular movement. In this case, the activity of the muscle is reduced or cancelled; electrostimulation, applied locally, is then used to prevent muscle atrophy.
In the field of sports, electrostimulation combined with a series of voluntary exercises can achieve the same kind of objectives. In fact, this technique of combining the two exercises, involuntary and voluntary, increases the benefits of your physical preparation.
In addition, this technique can help the muscle relax. To do this, the machines are equipped with a specific program. This relaxation accelerates muscle recovery.
3. EMS involves a greater number of muscle fibers than conventional training.

Electrostimulation, as practiced in the gym or even at home, is a global electrostimulation. It is done with a jacket or a neoprene suit. This combination connects the participant to the machine or device that sends the current through wires. This involuntary exercise is in addition to the voluntary exercise you would do if you were following the instructor’s instructions.
This stimulation contracts more muscle fibers than during a traditional physical training. We get tired faster, that’s why the sessions are short and last only 20 minutes.
This is the equivalent of 4 hours of traditional sports: an incomparable saving of time and efficiency!
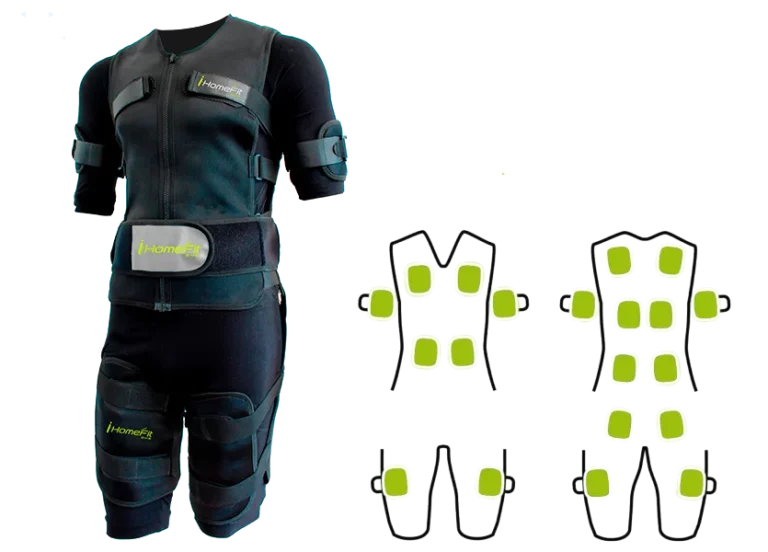
4. Electrostimulation is performed using a vest equipped with electrodes.
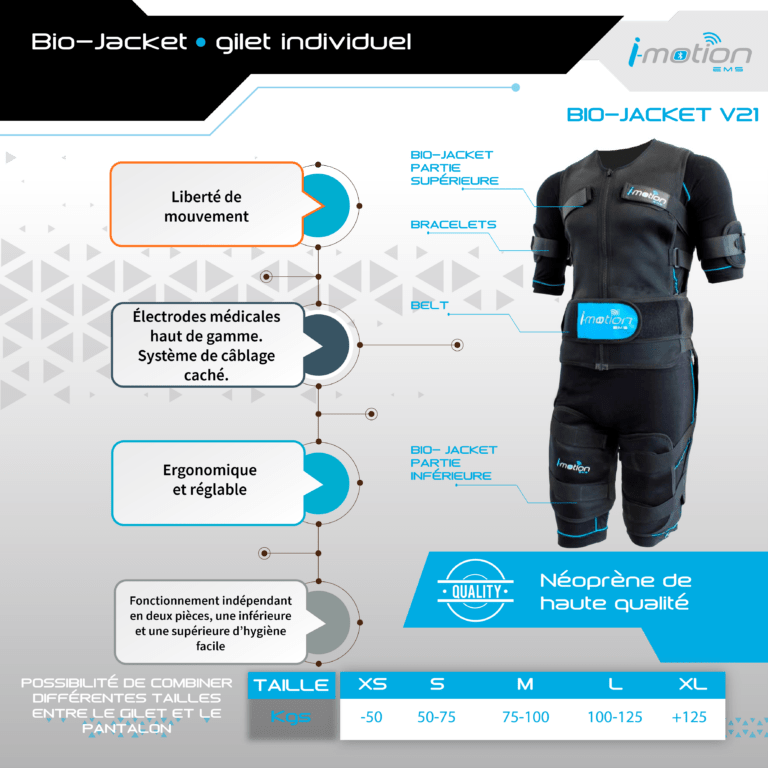
The electrostimulation vest is equipped with electrodes placed in strategic locations to trigger muscle contraction. Under the jacket, the athlete wears cotton leggings and a cotton t-shirt that must remain wet to transmit the current. Cotton is the most recommended fabric. The vest is fitted to the body with bands for greater freedom of movement.
Inside, the electrodes are distributed so that the muscle is correctly stimulated.
The machine or console regulates the intensity of the impulses that will be transmitted to the muscles by the electrodes, with a regular frequency. The intervals will be a few seconds long, the time for the muscle to recover after the contraction.
The electrodes can be adjusted independently on the machine. Thanks to our top of the line software, you can also take advantage of the numerous pre-set programs according to your goal.
Many top athletes use electrostimulation during their training sessions, discover the testimony of Laura Ziv, bodybuilding champion, here.
5. "electro fitness : more strength, speed and power
In athletes, frequent use of electrostimulation improves strength, speed and power.
This exercise does not cause any joint damage. Exercising with electrostimulation does not cause any joint damage because there is no load on the joints.
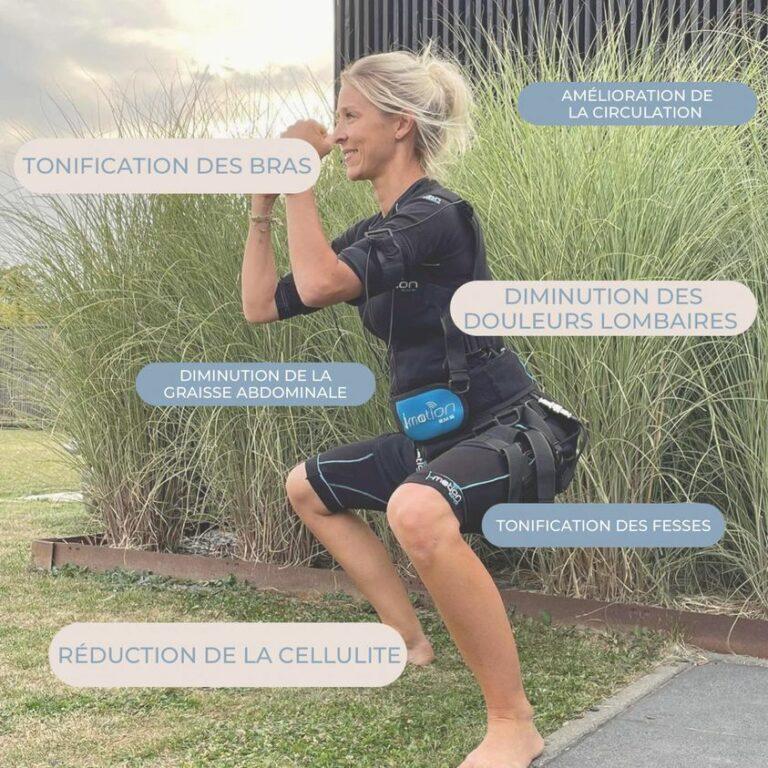
Electrostimulation promotes localized fat loss and increases metabolism.
One of the advantages of electrostimulation is the afterburner effect. In fact, after training, the body continues to burn fat by increasing the basal metabolic rate. This effect occurs over a period of three days.
6. EMS Contributes to Weight Loss
Electrostimulation contributes to weight loss, especially if it is accompanied by exercises. This helps your body to accelerate the fat burning process.
The muscles will be more toned and harder, which increases the consumption of calories. A stronger muscle allows you to perform your usual electro-stimulation exercises with more intensity and burn more calories.
7. EMS helps to fight against sagging
The skin is subjected to all sorts of aggressions, such as excessive exposure to the sun. Its appearance deteriorates mainly due to a decrease in the production of collagen and elastin.
The positive effects are numerous and sometimes unsuspected:
- Electrostimulation allows you to regain a smoother skin in the muscles, buttocks, abdomen and arms.
- This technique activates the blood circulation.
- The blood circulates better and irrigates the subcutaneous tissues more, which helps prevent the effects of aging and improves the appearance of the skin.
To learn more about electrostimulation in the field of aesthetics, consult our Aesthetics Pack.
8. The benefits of electrostimulation are holistic.
This means that these are not isolated benefits, but that the overall well-being brought by the practice of electrostimulation is the result of all these benefits. Each of them has its own advantages and makes this training so amazing in terms of results obtained.

your turn!
If you would like to know more about electrostimulation, consult our equipment pages.






